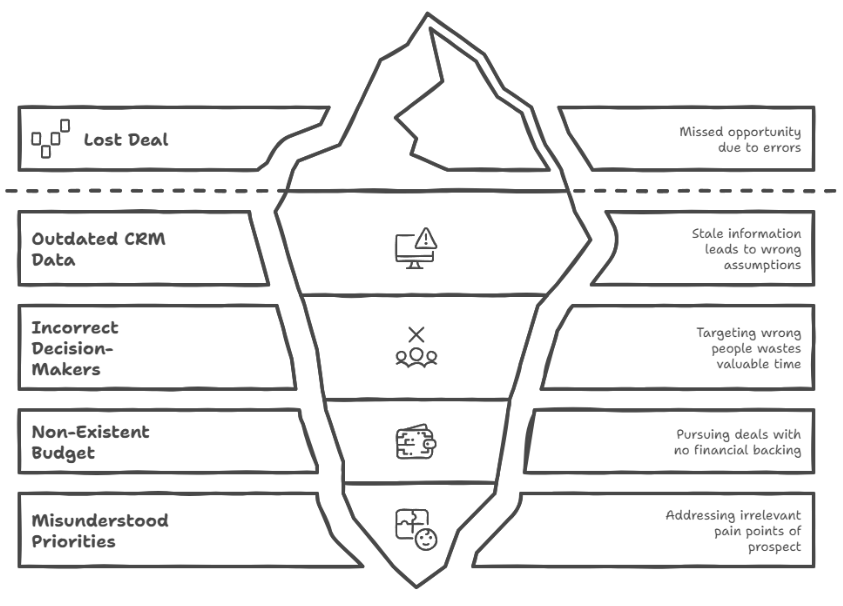
Two years ago, my sales team was riding high after landing what seemed like our ideal prospect – a fast-growing fintech company that checked every box on our ideal customer profile. Our CRM showed a company with 250 employees, $50M in annual revenue, and a tech stack that perfectly matched our solution. The initial conversations went smoothly, the demo was well-received, and we were confident about closing a $3.2 million multi-year deal.
But three weeks into the sales process, everything started falling apart in ways that made no sense. The technical stakeholders we’d identified weren’t the actual decision-makers. The budget we’d been told about didn’t exist in the current fiscal year. The pain points we’d been addressing weren’t actually their biggest priorities. Most embarrassingly, the “CTO” we’d been pitching to had left the company six months earlier, and our contact had been too polite to correct us.
What we thought was a perfect lead was actually a house of cards built on outdated, incomplete, and flat-out wrong information. Our CRM data was 18 months old. The company had gone through a major restructuring, changed their technology priorities, and shifted their business model – none of which our “comprehensive” database had captured. We were essentially pitching a solution for a company that no longer existed.
That near-disaster became the wake-up call that transformed our entire approach to B2B sales. We implemented a comprehensive data enrichment strategy that automatically updates prospect information, identifies key decision-makers in real-time, and tracks organizational changes as they happen. The same fintech deal that nearly slipped away ultimately closed six months later, but only after we rebuilt our relationship from scratch using accurate, current data.
More importantly, that experience revealed a truth that most B2B sales teams refuse to acknowledge: in today’s rapidly changing business environment, your data is probably wrong, your assumptions about prospects are likely outdated, and your sales strategy is built on a foundation of outdated information that’s costing you deals every single day.
To learn more about data enrichment in a B2B environment visit https://connexy.com/
The Hidden Cost of Bad Data (It’s Worse Than You Think)
Most sales leaders know their data isn’t perfect, but they dramatically underestimate how much bad data is actually costing them. It’s not just about a few missed opportunities or embarrassing moments in sales calls – poor data quality creates a cascade of problems that touches every aspect of your sales operation.
Wasted sales effort is the most obvious cost, but it’s often calculated incorrectly. Sales teams focus on the time spent pursuing unqualified leads, but the real cost is opportunity cost – the qualified prospects they didn’t pursue because their time was consumed chasing bad leads. When your best sales rep spends three weeks pursuing a “high-value” prospect that was never going to buy, you lose more than those three weeks of salary. You lose the other deals that rep could have been closing.
Damaged credibility with prospects can kill deals before they start. When you reach out to someone who left the company months ago, reference outdated information about their business, or propose solutions for problems they’ve already solved, you signal that you don’t do your homework. That first impression shapes every subsequent interaction and often eliminates you from consideration regardless of how good your solution might be.
Misaligned sales strategies develop when your entire go-to-market approach is based on inaccurate market intelligence. If your data shows that companies in a certain sector are using technology they’ve actually moved away from, or indicates budget priorities that shifted six months ago, your entire sales approach becomes irrelevant. You end up perfectly executing the wrong strategy.
Why Traditional Sales Intelligence Falls Short
Most B2B sales teams think they have good data because they’re using established providers or comprehensive databases. But traditional sales intelligence approaches were designed for a slower-moving business environment and simply can’t keep pace with how quickly modern companies change.
Static database problems plague most traditional providers. Even the best databases are essentially snapshots of information that become outdated the moment they’re compiled. Companies change employees, shift strategies, modify technology stacks, and restructure operations constantly. A database that was accurate six months ago might be wrong about 40-60% of key details today, especially for growing companies that change rapidly.
Contact information decay happens faster than most sales teams realize. Studies show that B2B contact databases degrade at rates of 25-30% annually, but for high-growth companies and emerging sectors, the decay rate can exceed 50%. Even worse, the most valuable contacts – senior decision-makers and technical stakeholders – tend to change roles more frequently than average employees, making the most important data least reliable.
Organizational structure blindness affects most traditional data sources because they focus on official org charts rather than actual decision-making structures. The database might correctly show that someone has the title “VP of Technology,” but miss that purchasing decisions actually flow through operations, or that budget approval requires sign-off from a shared services team that doesn’t appear in any public directory.
How Data Enrichment Actually Works (Beyond the Marketing Hype)
Real data enrichment goes far beyond appending phone numbers and email addresses to your contact lists. Effective data enrichment creates a dynamic, constantly updated view of your prospects that reflects current business reality rather than historical snapshots.
Multi-source verification ensures accuracy by comparing information across multiple independent sources rather than relying on single databases. If three different sources confirm that someone changed jobs, but one source still shows them at their old company, the enrichment system flags the discrepancy for verification rather than simply accepting whichever source was checked first.
Real-time trigger monitoring watches for changes that affect sales opportunities – new funding rounds, executive changes, technology implementations, office expansions, regulatory filings, or strategic announcements. This goes beyond basic news monitoring to identify events that specifically impact the likelihood of a buying decision or change sales strategy requirements.
Technographic enrichment analyzes the actual technology stack companies use rather than relying on self-reported information or outdated surveys. This includes identifying specific software versions, implementation timelines, and technology refresh cycles that affect when companies might be ready to evaluate new solutions.
Building a Data Enrichment Strategy That Actually Works
Successful data enrichment requires more than just buying tools and hoping for better results. The companies that see dramatic improvements follow systematic approaches that align data enhancement with specific sales objectives and measurement criteria.
Start with audit and assessment of your current data quality to understand exactly where gaps and inaccuracies are costing you deals. I recommend analyzing your last 50 lost opportunities to identify how many were affected by data quality issues – wrong contacts, outdated company information, missed organizational changes, or inaccurate assumptions about technical requirements.
Define enrichment priorities based on which data gaps have the highest impact on sales performance. For most B2B companies, this means prioritizing accurate contact information for decision-makers, current technology stack details, recent organizational changes, and real-time intent signals. Don’t try to enrich everything at once; focus on the information that most directly affects deal outcomes.
Integration strategy should connect enrichment tools with your existing sales stack to create automated workflows rather than manual processes. The best implementations update CRM records automatically, trigger sales alerts when important changes occur, and provide enriched information within the tools sales reps already use daily.
Real Success Stories: Data Enrichment in Action
The transformation that data enrichment can create becomes clear when you see how it affects actual sales performance in competitive B2B environments. These examples show the practical impact of moving from static databases to dynamic, enriched intelligence.
A cybersecurity software company was struggling with 18-month sales cycles and 12% close rates despite having a superior technical solution. Their problem was timing – they were reaching out to prospects randomly rather than when those prospects were actively dealing with security issues or evaluating new solutions. After implementing intent data enrichment that identified companies researching cybersecurity solutions, their average sales cycle dropped to 8 months and close rates increased to 28%. More importantly, they could focus sales efforts on prospects who were actively in-market rather than trying to create demand from scratch.
A marketing automation platform increased their average deal size by 185% by using technographic enrichment to identify prospects using multiple disconnected tools that could be consolidated into their integrated platform. Instead of selling basic automation features, they could lead with enterprise consolidation strategies that addressed real integration challenges prospects were experiencing. The enriched data revealed upsell opportunities that weren’t visible from basic firmographic information.
The Real ROI: What Data Enrichment Actually Costs vs. What It Returns
The financial impact of data enrichment becomes clear when you calculate the true cost of poor data quality and compare it to the investment required for comprehensive data enhancement. Most sales leaders dramatically underestimate both sides of this equation.
Direct cost analysis should include the obvious expenses – enrichment tool subscriptions, integration costs, and training time – but also opportunity costs like deals lost to poor data quality, sales rep productivity losses from bad leads, and marketing spend wasted on outdated target lists. For most B2B companies with sales teams larger than 10 people, bad data costs exceed $500,000 annually in wasted effort and lost opportunities.
Revenue impact calculations need to account for increased conversion rates, shorter sales cycles, larger deal sizes, and improved sales rep productivity. Companies that implement comprehensive data enrichment typically see 25-40% improvements in key sales metrics within the first year. For a sales organization with $10M in annual revenue, this translates to $2.5-4M in additional sales.
Efficiency gains compound over time as sales teams spend less time on manual research and data verification, allowing them to focus on relationship building and closing deals. Most sales reps save 8-12 hours per week when data enrichment eliminates manual prospecting research, which can increase their activity levels by 30-50%.
Common Implementation Mistakes (And How to Avoid Them)
Most companies that fail to see results from data enrichment make predictable implementation mistakes that undermine the entire investment. Understanding these pitfalls helps ensure your implementation delivers the expected returns.
Tool overload happens when companies try to implement multiple enrichment solutions simultaneously without clear integration strategies. Different tools often provide conflicting information, creating confusion rather than clarity. Start with one primary enrichment platform and add additional tools only after the initial implementation is working smoothly.
Passive consumption treats enriched data as nice-to-have information rather than actionable intelligence that should change sales behavior. Sales teams continue using the same generic outreach approaches while ignoring the personalization opportunities that enriched data provides. Success requires training teams to modify their sales process based on enriched insights.
Quality assumption problems occur when teams stop validating enriched data because they assume automated sources are always accurate. Even the best enrichment tools have error rates of 5-15%, and specific data points can be significantly less reliable. Maintain validation processes for high-value prospects and important deal decisions.
The Future of B2B Sales Intelligence
Data enrichment capabilities are advancing rapidly, and understanding these trends helps position your sales organization to take advantage of emerging opportunities while avoiding investment in approaches that will become obsolete.
AI-powered enrichment will automate much of the manual verification and analysis that currently requires human intervention. Machine learning systems will continuously validate data accuracy across multiple sources, predict which prospects are most likely to buy based on enriched signals, and automatically personalize outreach messages using enriched insights.
Real-time intelligence will replace periodic database updates with continuous monitoring of prospect changes, market events, and buying signals. Sales teams will receive immediate alerts when prospects experience trigger events, change organizational structures, or show intent signals that indicate sales opportunities.
Making Data Enrichment Work for Your Sales Team
The companies that get the most value from data enrichment treat it as a strategic initiative rather than a tactical tool purchase. Success requires aligning enrichment capabilities with specific sales objectives and creating organizational processes that maximize the value of enhanced intelligence.
Start with clear objectives about what you want data enrichment to accomplish rather than just hoping for better results. Whether that’s shortening sales cycles, improving conversion rates, increasing deal sizes, or reducing acquisition costs, specific goals help you choose the right tools and measure success accurately.
Pilot programs allow you to test enrichment approaches with small segments of your sales process before rolling out organization-wide implementations. Test different enrichment providers, integration approaches, and usage strategies to identify what works best for your specific market and sales process.